What causes ringing in your ears?
Noise levels louder than a shouting match can damage parts of our inner ears called hair cells. Hair cells act as the gatekeepers of our hearing. When sound waves hit them, they convert those vibrations into electrical currents that our auditory nerves carry to the brain. Without hair cells, there is nothing for the sound to bounce off, like trying to make your voice echo in the desert.
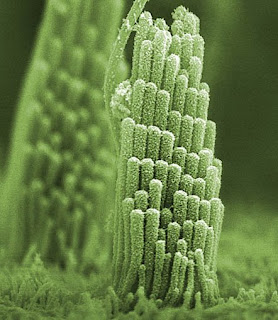
Hair cells reside in the inner ear inside the shell-shaped cochlea. Bundles of hair-like extensions, called stereocilia (shown above), rest on top of them. When sound waves travel through the ears and reach the hair cells, the vibrations deflect off the stereocilia, causing them to move according to the force and pitch of the vibration. For instance, a melodic piano tune would produce gentle movement in the stereocilia, while heavy metal would generate faster, sharper motion. This motion triggers an electrochemical current that sends the information from the sound waves through the auditory nerves to the brain. When you hear exceptionally loud noises, your stereocilia become damaged and mistakenly keep sending sound information to the auditory nerve cells. In the case of rock concerts and fireworks displays, the ringing happens because the tips of some of your stereocilia actually have broken off. You hear those false currents in the ringing in your head, called tinnitus. However, since you can grow these small tips back in about 24 hours, no real damage is done. From "How Stuff Works.com".
Hair cells reside in the inner ear inside the shell-shaped cochlea. Bundles of hair-like extensions, called stereocilia (shown above), rest on top of them. When sound waves travel through the ears and reach the hair cells, the vibrations deflect off the stereocilia, causing them to move according to the force and pitch of the vibration. For instance, a melodic piano tune would produce gentle movement in the stereocilia, while heavy metal would generate faster, sharper motion. This motion triggers an electrochemical current that sends the information from the sound waves through the auditory nerves to the brain. When you hear exceptionally loud noises, your stereocilia become damaged and mistakenly keep sending sound information to the auditory nerve cells. In the case of rock concerts and fireworks displays, the ringing happens because the tips of some of your stereocilia actually have broken off. You hear those false currents in the ringing in your head, called tinnitus. However, since you can grow these small tips back in about 24 hours, no real damage is done. From "How Stuff Works.com".
This question was posed by Robbie Hollis in Form IV.

Comments